Griffeath Model
This cyclic cellular automaton is a kind of automaton rule invented by David Griffeath from University of Wisconsin – Madison.
Standard version
This auto-reproductive cell automaton is two-dimensional, and its cells can take four states (1, 2, 3 or 4) in the standard version.
Description
The state of a cell at time t + 1 depends on its state at time t and the state of its 4 neighbors (Von Neumann's neighborhood).
A cell moves from a state i to a state i + 1 (mod 4) in the state cycle when the state i + 1 (mod 4) is present in at least one neighboring cell.
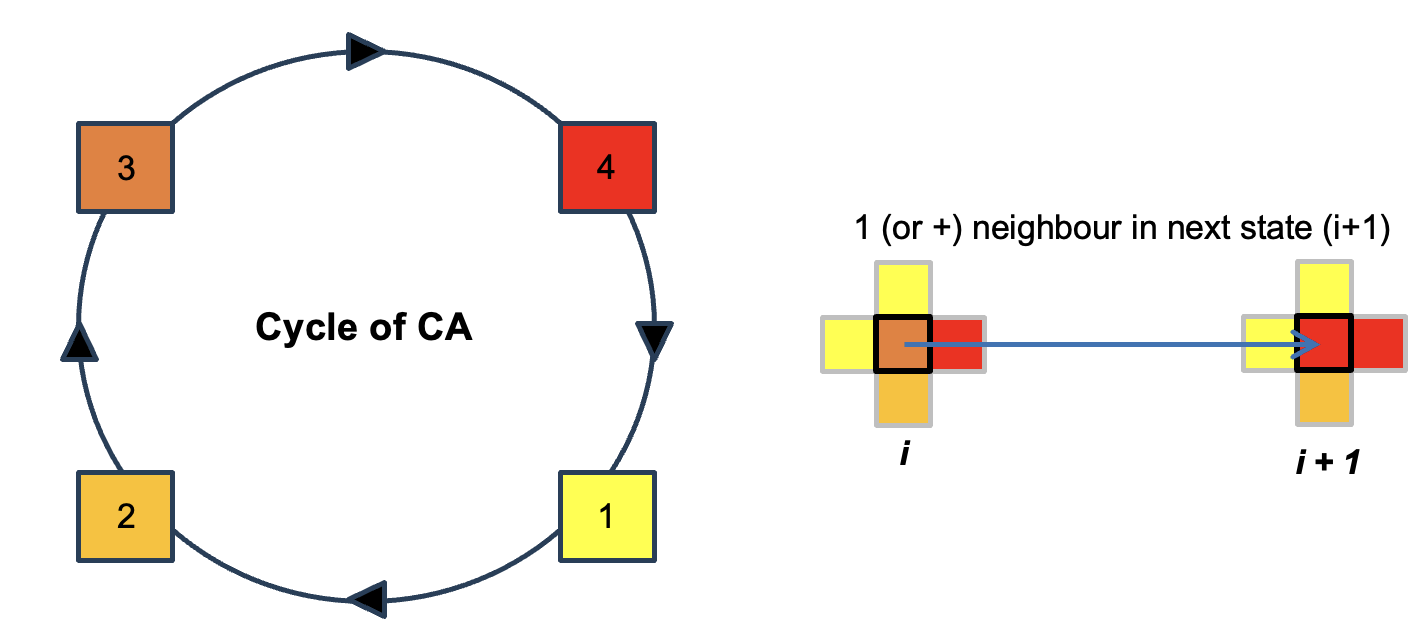
Run the standard version in Cormas
- Load the model
- Prepare the simulation:
- init method =
initRandomSpace_VonNeuman(4 neighbours) - step method =
stepStandard - click on the
Reinitialize simulationbutton, then - click on the
Runbutton You should get something like:
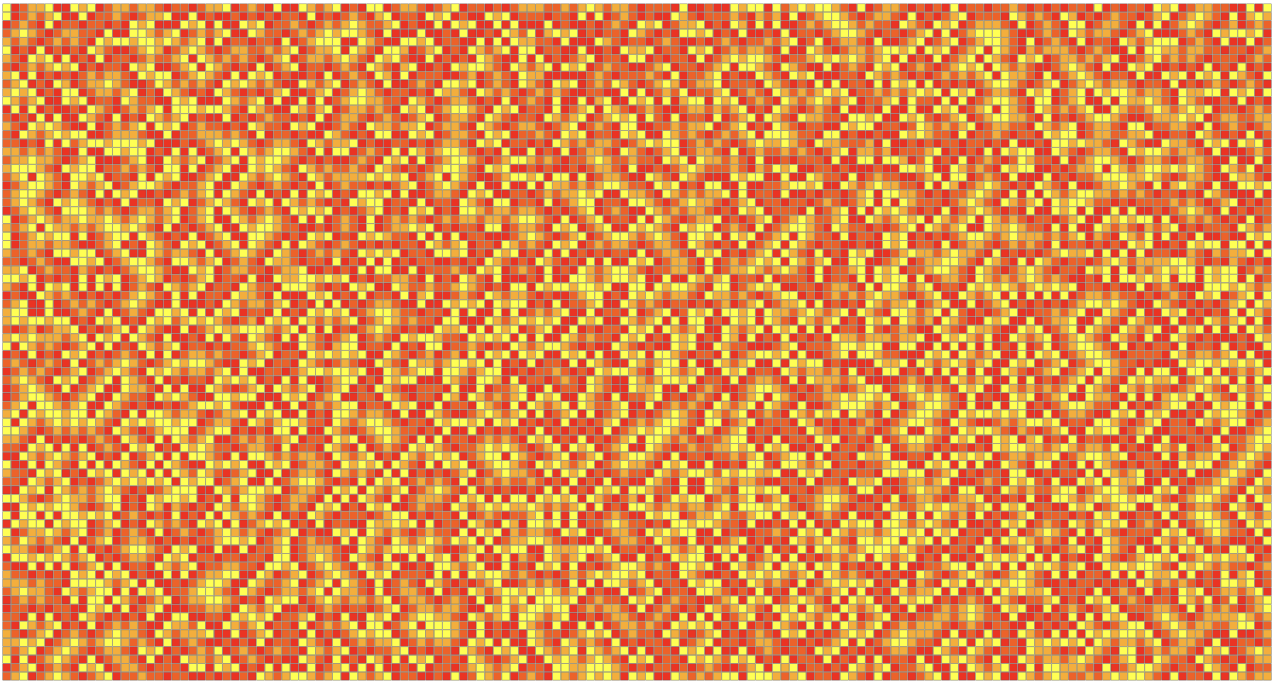 Example of space at step 200, with random seed fixed at 111
Example of space at step 200, with random seed fixed at 111
Version with threshold
Description
For 8 neighbors (Moore), Griffeath did modifications by adding a threshold (3 by default) for wich a cell changes its state:
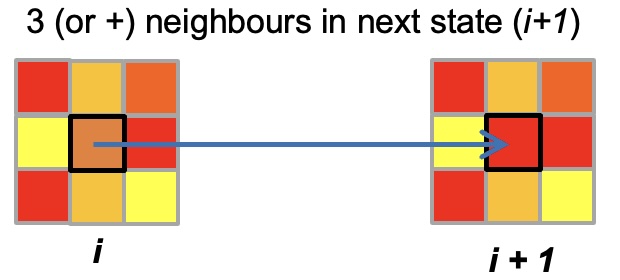
For this version, if you simulate with 5 states, you may observe such figure:
Run the version with threshold in Cormas
- Load the model
- Prepare the simulation:
- set the number of states to 5:
-
click on the
Parameter Editorbutton, and -
change the parameter
nbOfStatesfrom 4 to 5: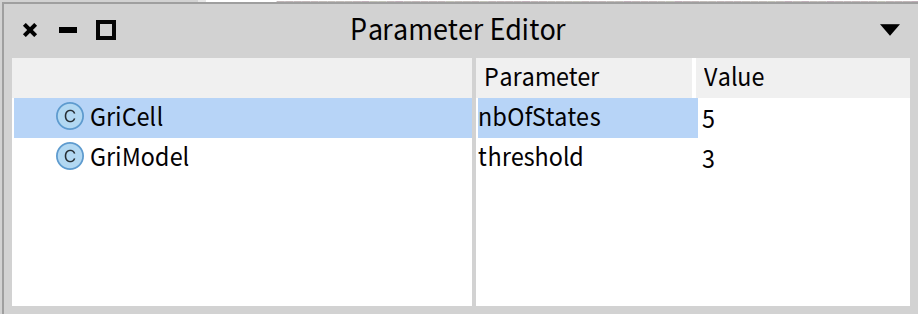
-
- init method =
initRandomSpace_Moore(8 neighbours) - step method =
stepThreshold - click on the
Reinitialize simulationbutton, then - click on the
Runbutton
You should get something like:
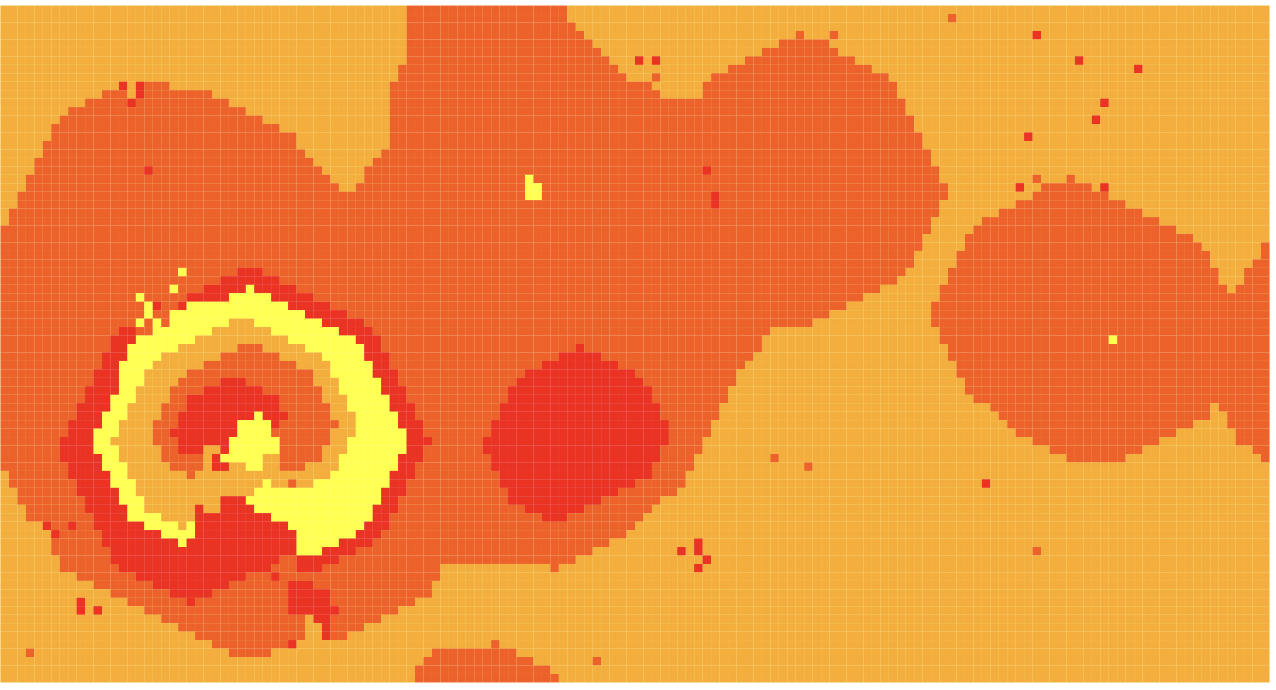
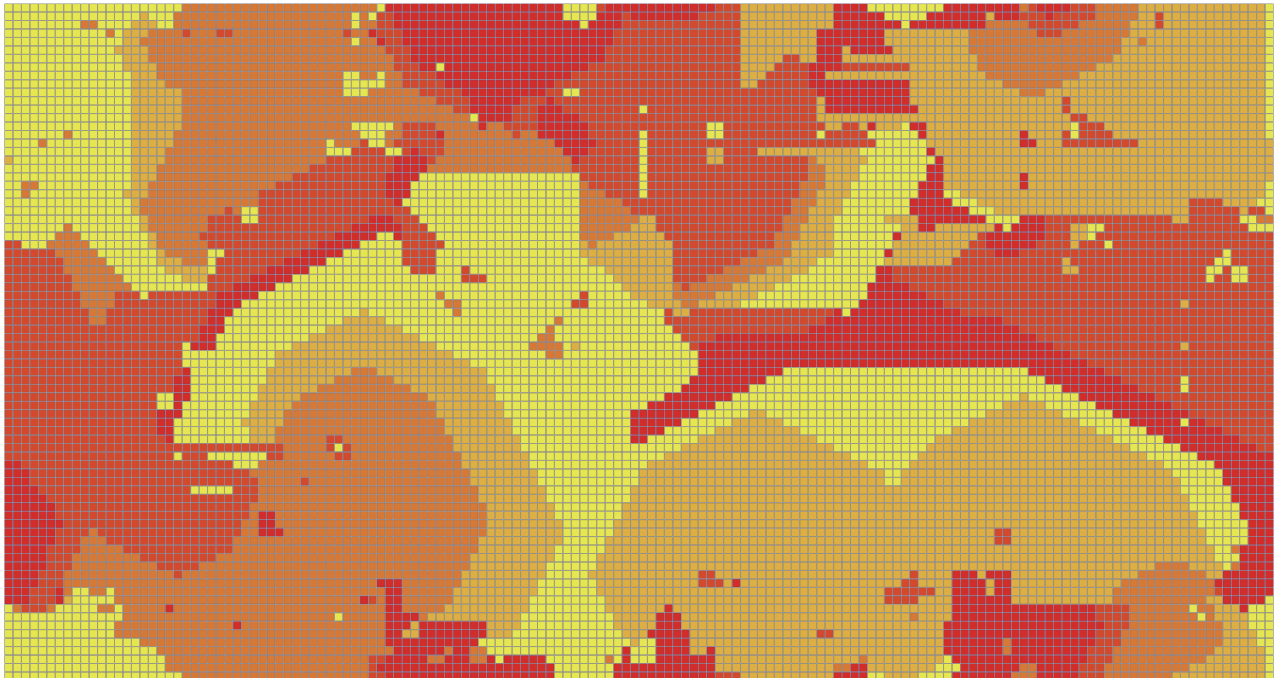 Example of space at step 370, with random seed fixed at 111054449681629184
Example of space at step 370, with random seed fixed at 111054449681629184
Version with range of states
The current cell in state i checks its state against the neighbors' states. If 3 (threshold) or more neighbors have a state between (i+1) and (i + nbStates/3), then the current cell changes to that state. For example, if the current cell state is 2, and 3 of its neighbors are in state 3 to 6, then the current cell changes its state to 3:

For this version, if you simulate with 14 states, you may observe such figure:
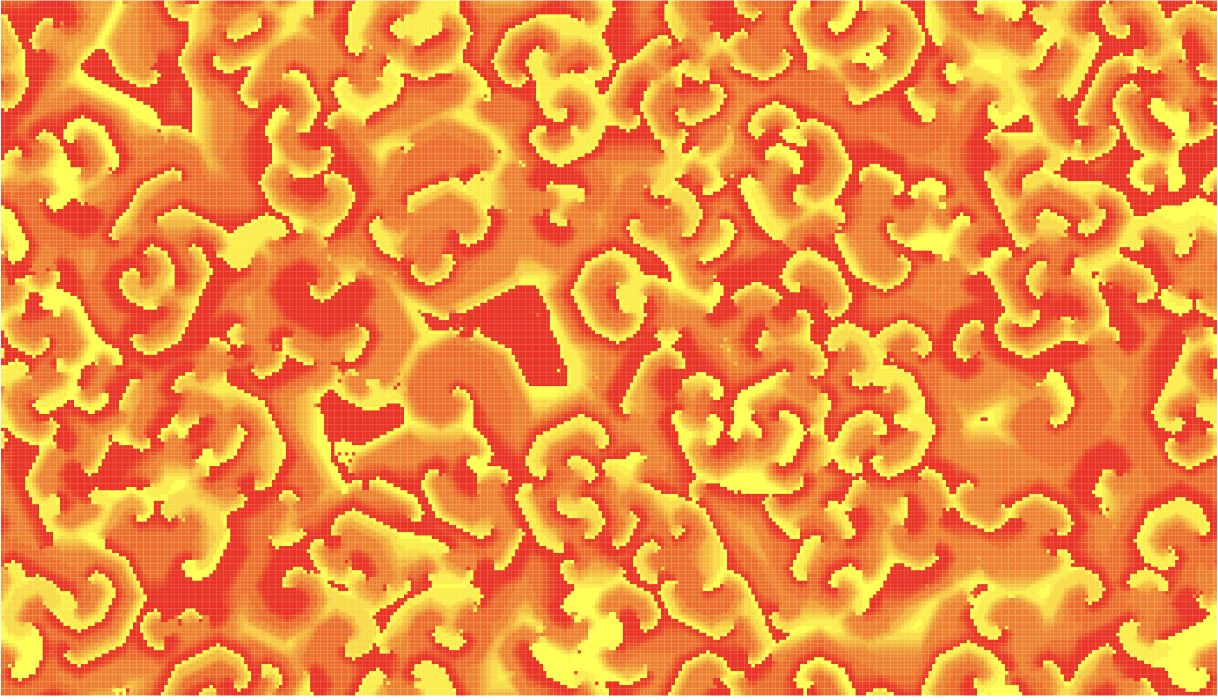
Run the version with range of states in Cormas
- Load the model
- Prepare the simulation:
- set the number of states to 5 (like previously)
- init method =
initRandomSpace_Moore(8 neighbours) - step method =
stepAverage - click on the
Reinitialize simulationbutton, then - click on the
Runbutton
You should get something like:
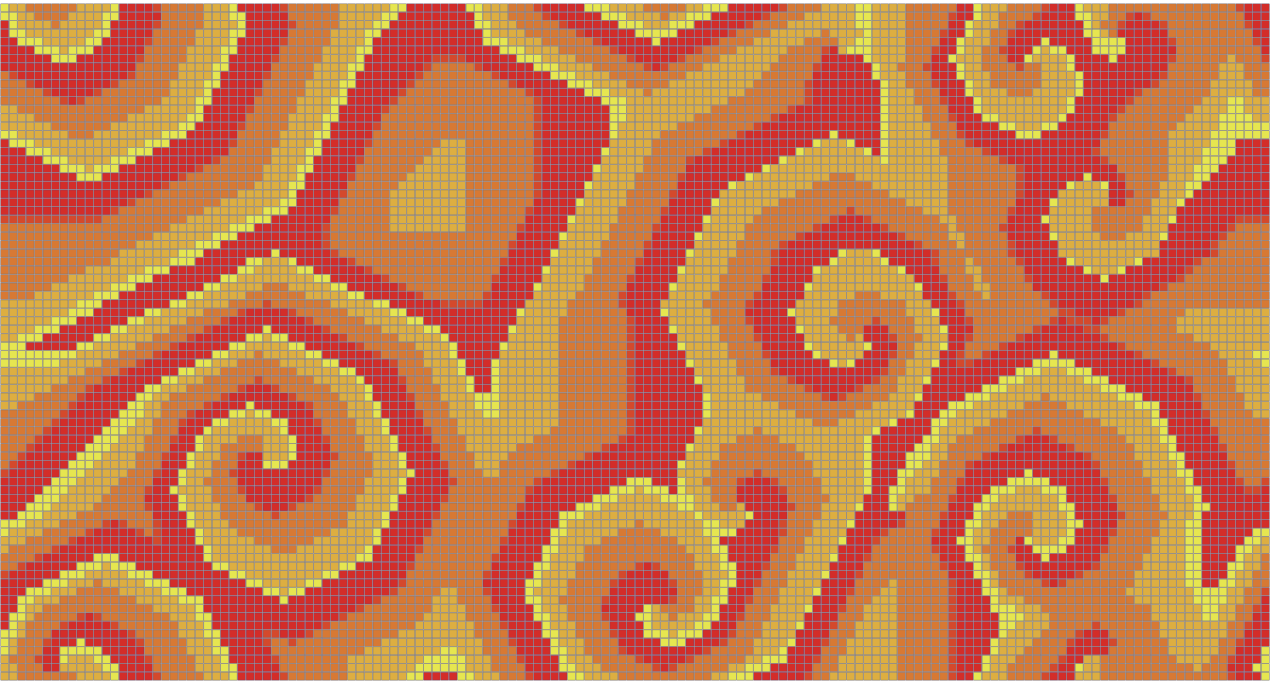 Example of space at step 370, with random seed fixed at 111054449681629184
Example of space at step 370, with random seed fixed at 111054449681629184